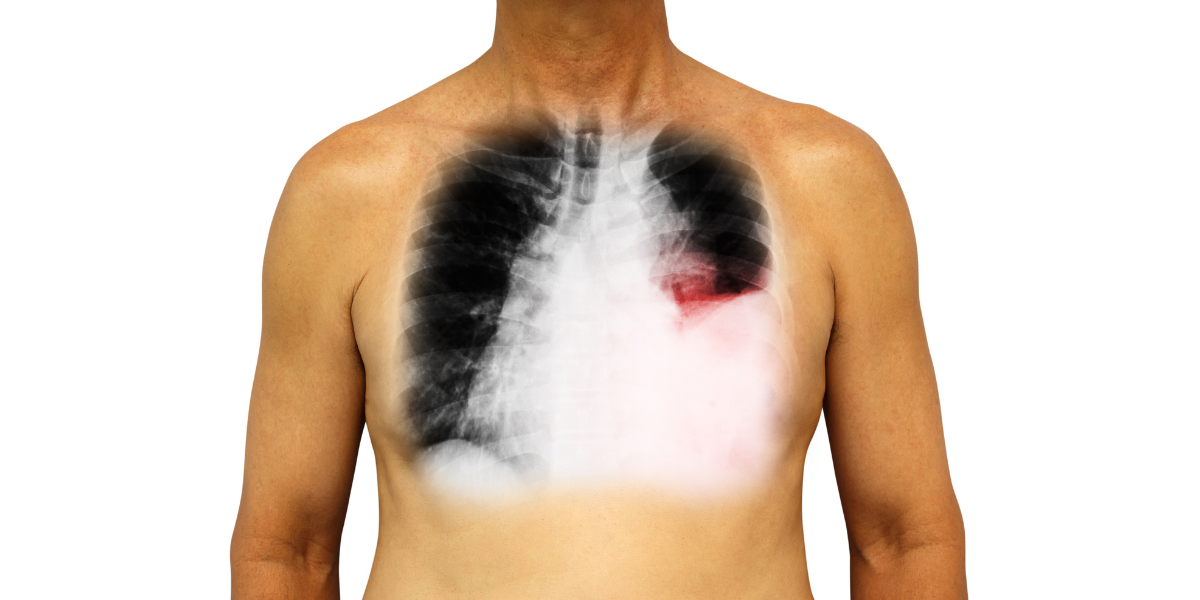
Pleural Effusion
Pleural effusion is a condition where excess fluid accumulates between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and chest cavity, known as the pleura. This buildup of fluid can cause symptoms such as chest pain, coughing, and shortness of breath. Pleural effusion can result from various underlying conditions, including heart failure, infections, lung cancer, and pulmonary embolism.
Diagnosis typically involves imaging studies like chest X-rays, ultrasounds, or CT scans to detect the presence of fluid. Further testing, including thoracentesis (removal of fluid with a needle), may be conducted to analyze the fluid and determine the underlying cause.
Treatment of pleural effusion depends on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms. It may include draining the fluid to relieve symptoms, treating the underlying medical condition, or using medications to prevent fluid re-accumulation. Early diagnosis and intervention are important to prevent complications and improve outcomes.